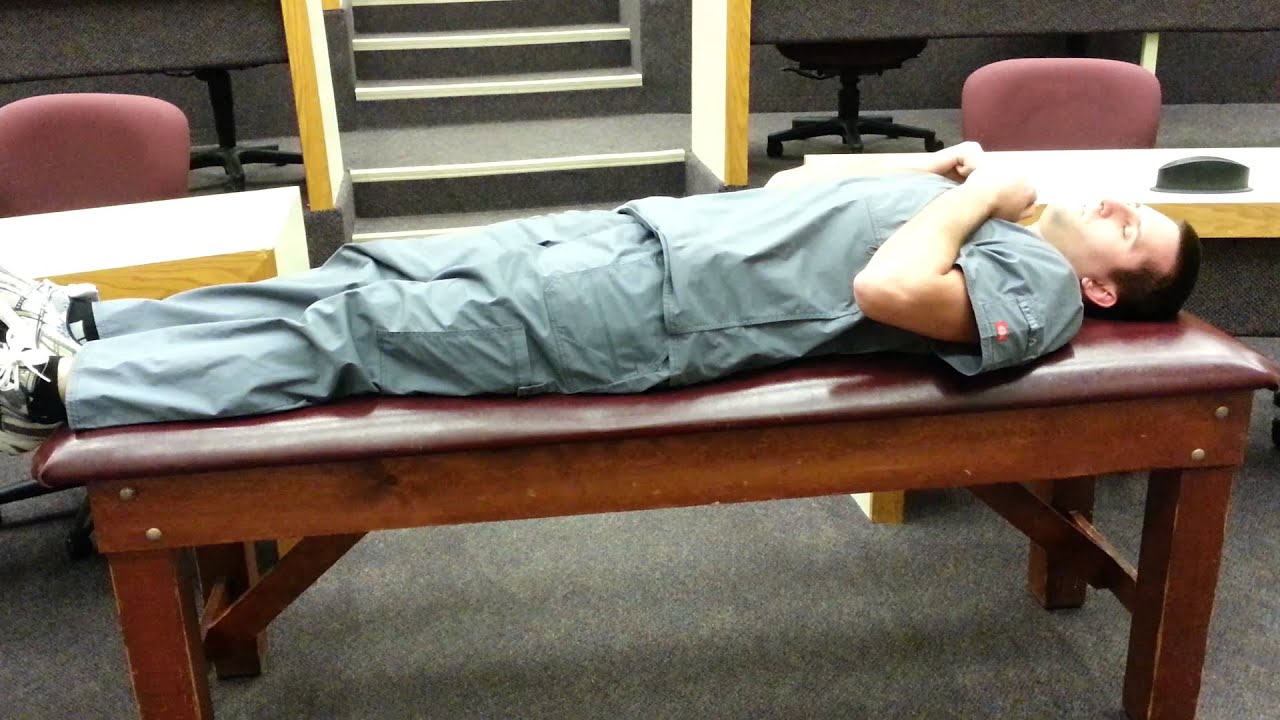
Unilateral Decorticate Posturing

Decorticate posture involves a form of posturing where a person s arms are bent and stiff their legs are straight out and their fists are clenched.
Unilateral decorticate posturing. Decorticate and decerebrate posturing refers to primitive stereotyped motor responses exhibited by patients with severe brain injury. Decorticate posturing is a posturing that indicates a severe damage in the brain. Decerebrate rigidity may be elicited by noxious stimuli or may occur spontaneously.
Unilateral dystonic posturing of an upper extremity is an interesting phenomenon that occurs typically in seizures of temporal lobe origin. Unilateral decerebrate or decorticate postures can be seen and are an indication of a unilateral lesion. Due to structural lesions of the thalamus internal capsule or cerebral white matter.
Decorticate posture is also a sign of severe damage to the person s brain. Their arms are bent in towards their body and their fingers and wrists are bent and held onto their chest. The feet are plantar flexed.
With concurrent brain stem and cerebral damage decerebrate rigidity may affect only the arms with the legs remaining flaccid. Patients with decorticate posturing present with the arms flexed or bent inward on the chest the hands are clenched into fists and the legs extended and feet turned inward. The two postures may also alternate as the patient s neurologic status fluctuates.
Decorticate posture this refers to bilateral flexion of the upper limbs and extension of the lower limbs usually the consequence of an upper brain stem lesion. Decorticate posturing is also called decorticate response decorticate rigidity flexor posturing or colloquially mummy baby. The patient exhibits bilateral adduction of the shoulders pronation and flexion of the elbows and wrists and extension internal rotation and plantar flexion of the.
This abnormal posturing makes a person suffer from clenched fists bent arms and legs that are held out straight. However this is not as serious as decerebrate posture wherein the particular kind of posturing appears on both sides of one s body. Alternatively decerebrate rigidity may affect one side of the body and decorticate rigidity the other.